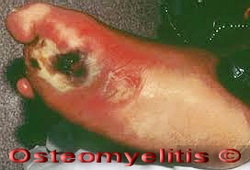
Osteomyelitis is a type of bacterial bone infection that moves from acute to chronic phases quickly. The infection usually begins in another part of the body and spreads to the bone via blood. Traumatic injury, frequent medication injections, the use of a prosthetic device, and some surgical procedures can increase susceptibility to the underlying infection. With osteomyelitis, the infected bone fills with pus that deprives the bone of its needed blood supply. Over time, this can result in the death of bone tissue. The presence of bone infection can be diagnosed with tests, such as bone scans and MRI. Osteomyelitis infections are very difficult to cure with oral or intravenous antibiotics. In chronic cases, surgical removal of the dead bone tissue is usually required.



