Stress fractures are a type of overuse injury. These tiny cracks in bones develop when muscles become overtired (fatigued) and can no longer absorb the shock of repeated impacts. When this happens, the muscles transfer the stress to the bones, creating a small crack or fracture. Stress fractures also can occur with normal usage if osteoporosis or some other disease weakens bones and leaves them vulnerable. These fractures are often called “insufficiency fractures” because there isn’t enough bone to withstand the normal stress of daily use.
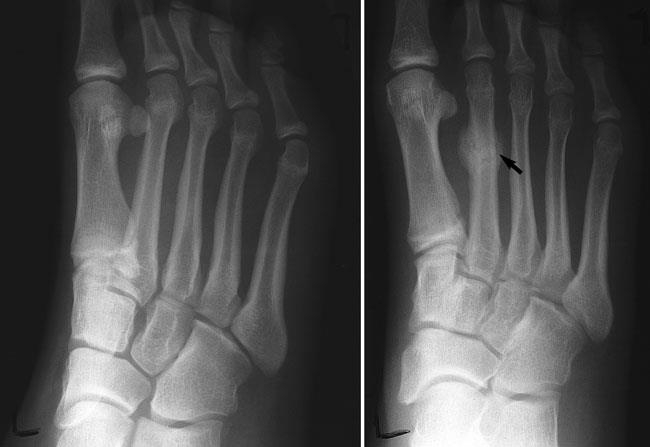
Most stress fractures occur in the weight-bearing bones of the foot and lower leg. The most commonly affected site is the second or third of the long bones (metatarsals) between the toes and the midfoot. Stress fractures also can occur in the heel, the outer bone of the lower leg (fibula) and the navicular, a bone on the top of the midfoot.
Commonly affected peoples:-
- Athletes who participate in high-impact sports such as track and field, basketball, gymnastics, ballet or tennis.
- Adolescents whose bones have not yet fully hardened.
- Women, particularly female athletes, who have abnormal or absent menstrual cycles that can result in decreasing bone mass.
- Military recruits who suddenly must shift from a sedentary civilian life to a more active training regime.
If suspect a stress fracture in foot or ankle, stop the activity and rest the foot. Ignoring the pain can have serious consequences, and the bone may break completely. Apply an ice pack and elevate the foot above the level of heart. Try not to put weight on the foot until after see a Foot and Ankle Surgeon. Stress fractures are difficult to see on X-rays until they’ve actually started to heal. Recommend a bone scan, which is more sensitive than an X-ray and can detect stress fractures early. Treatment will depend on the location of the stress fracture. Most stress fractures will heal if reduce level of activity and wear protective foot wear for 2 to 4 weeks. You may recommend that you wear a stiff-soled shoe, a wooden-soled sandal, or a removable short leg fracture brace shoe. Athletes should switch to a sport that puts less stress on the foot and leg. Swimming and bicycle riding are good alternative activities.



